Suitable plastics
The types of plastic commonly common in fast mold are thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics, and some elastomers. The materials available are often metals or a mixture of materials, so designers can select the material with the most suitable properties.

Material selection criteria are based on stiffness, modulus of elasticity, flexural resistance, heat resistance and water absorption, design requirements as well as manufacturing costs, each with different specifications. Should be considered and considered. The thermoplastics are nylon, polyethylene and polystyrene. Thermosetting resins are epoxy and phenolic.
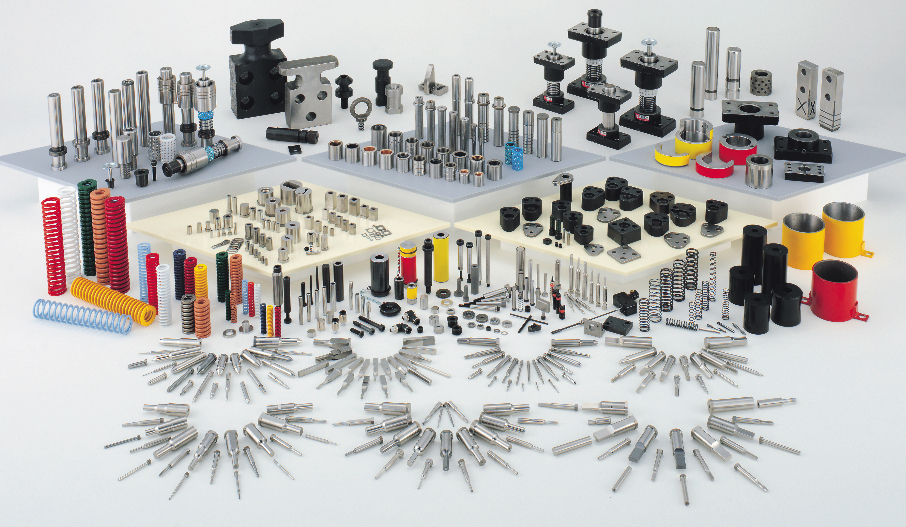
Equipment for fast mold
In fast mold, there is an injection molding machine consists of a feed hopper, a syringe or a spiral groove piston and a heating element. Presses are rated based on load capacity, i.e. the number of tightening torques that the machine can perform. This force helps to stabilize the mold during injection.
If the injection plastic is too hard, the injection force into the mold needs to be very large, so it is necessary to clamp the mold firmly so that the process can take place smoothly. The value of the force depends on the material and the size of the part. Larger sizes require greater tightening force.
Mold
The choice of fast mold material is often economical, steel molds cost more but their long life will offset the upfront cost and produce more parts before they wear out. Good steel is less prone to wear, suitable for the requirements of small volume parts, or larger parts, Aluminum molds can save costs.
Furthermore being able to cast hundreds of thousands of parts. Beryllium copper alloys are common when casting requirements require rapid heat dissipation.
Fast Mold design
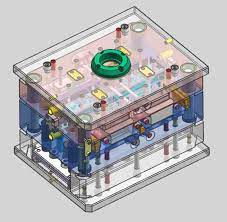
The casting fast mold consists of two main parts: the injection mold and the push mold, also known as the negative mold and the positive mold. Flexible plastic follows the nozzle through the nozzle and enters the mold cavity. The nozzle is the connection between the nozzle and the plastic channel.
The amount of resin required to fill the nozzles, channels and cavities calls a “shot”. The trapped air can escape through the vents connected at the mold divider, around the push pin, etc.
How product is removed from the mould?
To take the product out of the fast mold the mould usually has an empty corner for easy removal of the product from the mold. The blank angle is not large enough which can cause deformation or damage to the part. This clearance depends on the depth of the cavity; the deeper the mold, the more this blank corner is needed.
How temperature is maintained in fast mold?
The exhaust cooling system transports the coolant (usually water) through pipes connected to the mold plate to absorb the radiated heat and keep the mold at the right temperature for the most effective hardening of the material.
For ease of maintenance and ventilation, fast mold are often comes into several sections. By replacing, inserting or swapping, a mold is easy to mold into different forms of the same part.
What is the role of slides?
There is a Silde system (sliding platform) entering the cavity to push the protruding part. These pins touch the slide causing the platform to roll back when the movable mold part opens.
What is over mould?
Some fast mold allows re-molding of previously created parts, creating a new plastic base around the part, called over mould. This system is common to produce tires and wheels.
Preservation fast mold
Manufacturers spend a lot of money to maintain custom molds for a long time. Perfect temperature and humidity guarantee the lifetime of each fast mold.
Crafting materials
Tool steels are commonly common. Mild steel, aluminum, nickel or epoxy is only suitable for test runs or very short production processes. Modern hard aluminum (usually alloys 7075 and 2024) with suitable mold designs easily makes molds capable of casting more than 100,000 parts with proper curing.
Manufacturing fast mold
The two main mold making methods are: standard machining method and EDM. The standard machining method common to be the conventional mold making method. With the development of technology, CNC machining has become the main means to create complex molds with higher precision and save time than traditional fast mold.
Electrical spark machining is gradually being common, as well as for machining difficult shapes, or forming hard molds without heat treatment. EDM is a simple process in which an electrode (copper or graphite has been soaked in kerosene) is introduced very slowly into the mold surface. The electrode reversal of the voltage applied between the tool and the die causes erosion and forms the required surface.
Cost of fast mold
The number of fast mold casting cavities is directly correlated with the casting cost. Fewer chambers and fewer tools lead to lower initial production costs. Since the number of cavities plays an important role, it is the complexity of the molded product design.
This complexity includes many factors such as surface finish, tolerances, external or internal threads, fine detailing or number of cuts. In particular, cuts or additional tool properties will increase die costs, and core and cavity surfaces will also affect production costs.
Keep reading this article and learn everything you need to know about fast mold.
This material is widely common in the pulp and paper, mining, food and beverage industries.
General purpose technical parts common in heavy mechanical industry.
Among fast mold features stands out:
- Generally, Very low friction coefficient;
- Features strong noise absorption;
- Moreover, It does not corrode or oxidize;
- Similarly, It doesn't break, it doesn't crack;
- Moreover, Does not absorb water;
- Allows a wide range of working temperatures;
- In addition, provides long service life.
What are your competitive advantages of fast mold?
These sheets have excellent properties, in addition to being cost-effective, relevant to other materials on the market.
We list below some differentials of this material:
Impact resistance:
It is exceptional in terms of strength, the highest among all known plastic materials.
Chemical resistance:
Equivalent to PTFE at moderate temperatures. Resistant very well to all chemicals and biological attack.
Self-lubrication:
Present in its composition, self-lubrication makes the material free from maintenance and contamination.





