Injection molding is one of the most widely used manufacturing processes for producing plastic parts in large volumes. It involves injecting molten material into a mold to create parts with precise dimensions. While the injection molding machine itself is the centerpiece of this operation, a wide array of support machinery is equally important in ensuring efficient, consistent, and high-quality production. This blog will dive into the details of injection molding machines and the essential support machinery that enhances the process, covering the machinery's function, benefits, and role in production.
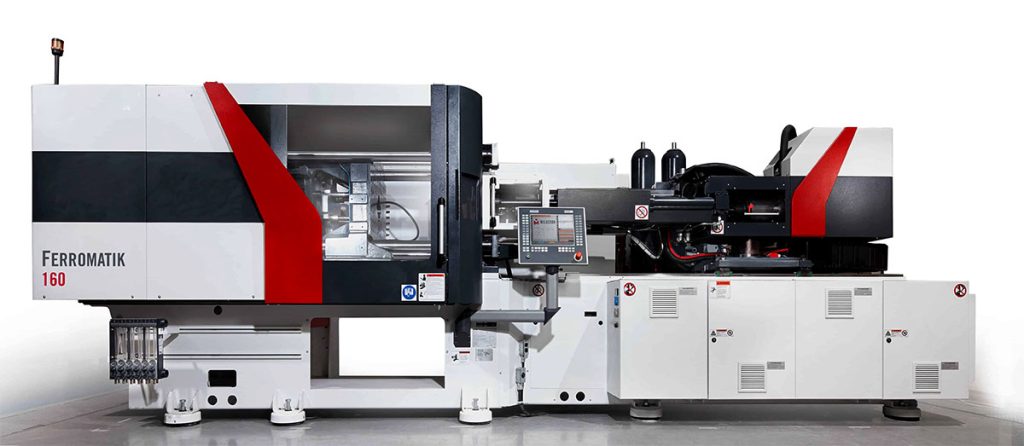

1. Injection Molding Machine Overview
At its core, an injection molding machine consists of three primary components:
- Injection Unit: This part is responsible for heating and injecting the plastic material into the mold. The plastic (typically in pellet or granule form) is fed into the machine’s hopper, melted by heaters, and pushed forward by a screw. The molten plastic is then injected into the mold cavity through a nozzle.
- Clamping Unit: The clamping unit holds the mold in place and applies the necessary force to keep the mold closed during the injection process. Once the material is injected, the clamping unit opens to release the molded part.
- Control Unit: Modern injection molding machines are equipped with advanced control systems that allow for precise adjustments to temperature, pressure, and timing. This precision is critical to ensure consistent quality in every part produced.
The machine can be powered by hydraulic, electric, or hybrid systems. Hydraulic machines offer higher clamping forces and are generally used for larger parts, while electric machines provide greater precision and energy efficiency, making them ideal for smaller, more intricate parts.
2. Types of Injection Molding Machines
There are various types of injection molding machines, each tailored for specific production needs:
- Hydraulic Injection Molding Machines: These are the traditional machines that use hydraulic pressure to power the clamping and injection processes. They are known for their high force and capability to handle large molds, but they are generally less energy-efficient compared to electric machines.
- Electric Injection Molding Machines: Electric machines use electric servo motors instead of hydraulic pumps, which provides better precision, energy savings, and faster cycles. They are ideal for high-precision, smaller parts like medical devices, electronics, and consumer goods.
- Hybrid Injection Molding Machines: These combine the benefits of both hydraulic and electric machines, offering high power where needed but also enhanced precision and efficiency.
- Two-Shot or Multi-Shot Injection Molding Machines: These machines allow for the molding of parts using two or more materials in a single process, often to create parts with multiple colors or materials with different properties.
3. Support Machinery in Injection Molding
In addition to the injection molding machine itself, support machinery plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient operations. These machines help optimize the molding process by improving material preparation, cooling, and part handling. Key support machinery includes:
a) Material Handling Equipment
The plastic material used in injection molding must be properly prepared and delivered to the machine. This requires various types of equipment:
- Dryers: Plastics, especially hygroscopic ones like nylon or polycarbonate, must be dried before being fed into the injection molding machine to prevent moisture-related defects. Desiccant dryers are commonly used to remove moisture by circulating heated air through the material.
- Hoppers: The hopper feeds the dried plastic granules into the injection unit. Some hoppers are equipped with loaders that automatically refill them as needed, ensuring a continuous supply of material.
- Conveyors: Conveyors transport raw materials from storage bins to the hopper and from the machine to the packaging area. Efficient material movement reduces downtime and enhances production efficiency.
b) Mold Temperature Controllers (MTCs)
Mold temperature control is crucial in achieving consistent part quality and reducing cycle times. Mold temperature controllers (MTCs) regulate the temperature of the mold during the molding process by circulating water or oil through channels in the mold.
Maintaining the correct temperature ensures that the plastic cools and solidifies at the right rate, which affects the part’s surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical properties. Too much heat can result in warping or shrinkage, while insufficient heat can cause incomplete fills or poor part quality.
c) Chillers
Chillers are essential in cooling the mold and maintaining the optimal temperature for the plastic to solidify quickly and correctly. They work by circulating chilled water through the mold’s cooling channels. Efficient cooling reduces cycle times and increases production output, making chillers indispensable for high-volume production runs.
d) Granulators and Shredders
Scrap plastic and defective parts are common by-products in injection molding. Granulators and shredders help recycle this material by breaking down the plastic into smaller granules, which can be reused in the molding process. This practice helps manufacturers reduce material costs and waste, promoting more sustainable production methods.
e) Robots and Automation Systems
Automation plays a significant role in modern injection molding processes, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Robots are commonly used to extract parts from the mold after each cycle. These robots can also handle tasks such as degating (removing excess plastic), trimming, and stacking the parts for packaging.
Automated systems also help with mold changes, part inspections, and packaging, allowing manufacturers to run their injection molding operations with minimal manual intervention. This reduces the risk of errors, increases consistency, and enables 24/7 production.
f) Hot Runner Systems
In injection molding, molten plastic flows through the sprue and runner system into the mold cavities. Traditional "cold runner" systems often leave excess plastic in the runners, which needs to be trimmed and discarded or recycled.
A hot runner system keeps the plastic within the runner system molten, which reduces waste and increases efficiency. Since there is no need to trim the runners, cycle times are reduced, and material is saved. Hot runners are often used in high-volume, precision-molding applications where minimizing waste and improving cycle times are essential.
4. Importance of Preventive Maintenance
Both injection molding machines and support equipment require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Preventive maintenance programs help avoid costly breakdowns, extend the lifespan of machinery, and improve overall production efficiency.
- Lubrication of Moving Parts: Injection molding machines have numerous moving components, including the screw, clamps, and injection units. Proper lubrication reduces wear and tear on these parts.
- Calibration: Regular calibration ensures that the control systems are operating correctly, maintaining precise temperatures, pressures, and cycle times.
- Cleaning: Mold cavities and the injection unit must be cleaned to prevent buildup that can cause defects or damage the mold.
- Inspection: Regular inspections of all support machinery help identify wear, leaks, or malfunctions that could impact production.
5. Final Thoughts
Injection molding is a complex process that requires not only an efficient and well-maintained injection molding machine but also a variety of support machinery to ensure smooth, cost-effective operations. From material handling equipment and mold temperature controllers to robots and hot runner systems, each piece of support machinery plays a vital role in optimizing production.





