Injection mold tooling is an essential part of modern manufacturing, allowing for the mass production of plastic parts with precision and efficiency. Whether you're developing consumer goods, automotive components, or medical devices, understanding how injection mold tooling works is crucial for ensuring high-quality results.
This guide explores everything you need to know about injection mold tooling, from its components and materials to cost considerations and future trends. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how to optimize your injection molding process for better efficiency and cost savings.
What is Injection Mold Tooling?
Injection mold tooling refers to the specialized equipment used to create plastic parts through injection molding. It involves a mold that consists of multiple components, which together shape and form the final product. The mold tooling is carefully engineered to withstand high temperatures and pressures while ensuring precise part dimensions.
A properly designed mold ensures consistency, minimizes material waste, and enhances production efficiency. However, designing and manufacturing injection molds require significant investment in both time and money. Choosing the right materials and mold type is essential to maximize durability and cost-effectiveness.
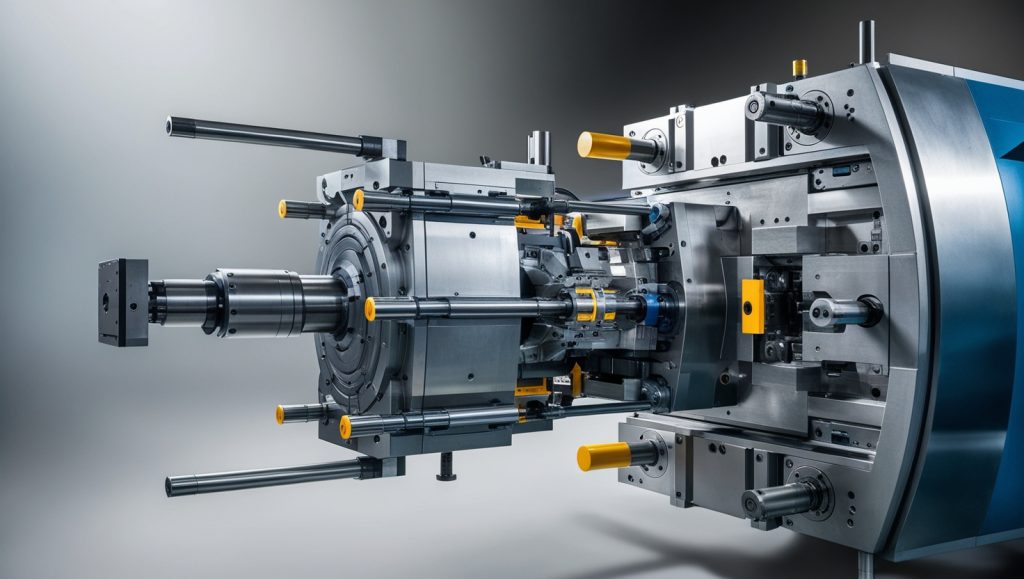
Key Components of Injection Molds
An injection mold consists of several key components that work together to form plastic parts. Each component plays a crucial role in determining the quality and efficiency of the molding process.
- Mold Base: The frame that holds all the mold components in place. It provides structural support and ensures proper alignment during molding.
- Cavity and Core: The primary forming sections of the mold, where the molten plastic takes its shape. The cavity forms the outer surface, while the core shapes the inner features.
- Runner System: Channels that guide molten plastic from the injection unit to the mold cavities. A well-designed runner system optimizes material flow and reduces waste.
- Gates: Entry points where the molten plastic enters the mold cavity. Different gate designs affect the quality of the final product.
- Cooling System: Circulates coolant through the mold to regulate temperature. Effective cooling reduces cycle time and minimizes defects.
- Ejection System: Mechanisms such as ejector pins or plates that remove the molded part from the mold. Proper ejection ensures smooth production without damaging the parts.
Types of Injection Mold Tooling
There are several types of injection molds, each designed for specific applications. Choosing the right mold type depends on production volume, complexity, and cost constraints.
- Prototype Molds: Used for testing and low-volume production. These molds are typically made of aluminum or soft steel and are less expensive than production molds.
- Production Molds: Designed for high-volume manufacturing, these molds are made from hardened steel for long-lasting durability.
- Single-Cavity Molds: Produce one part per cycle, ideal for low-production runs or large components.
- Multi-Cavity Molds: Contain multiple identical cavities, allowing for higher production efficiency and reduced per-unit cost.
- Family Molds: Feature multiple cavities for different parts within the same mold, commonly used for sets of components.
- Hot Runner Molds: Use heated channels to keep plastic molten, minimizing material waste and improving cycle time.
- Cold Runner Molds: Use unheated channels, leading to more material waste but lower mold costs.
Injection Mold Tooling Materials
The choice of material for injection molds significantly affects their performance, lifespan, and cost. The most common materials include:
- Hardened Steel: Highly durable and suitable for long production runs. It offers excellent wear resistance but is expensive.
- Pre-Hardened Steel: Less durable than hardened steel but more cost-effective for medium-volume production.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and suitable for prototype and low-volume molds. Aluminum molds offer faster machining and cooling times.
- Beryllium-Copper Alloy: Used in high-wear areas to improve heat dissipation and extend mold life.
Selecting the right material depends on the expected production volume, precision requirements, and budget constraints.
Mold Design Considerations
The design of an injection mold plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient production and high-quality parts. Several factors must be considered during the design process.
- Part Complexity: Complex designs require multi-part molds, increasing cost and production time.
- Material Selection: Different plastics have varying shrinkage rates, cooling requirements, and flow properties.
- Tolerances and Precision: High-precision parts require tighter tolerances, impacting mold complexity.
- Cooling and Venting: Proper cooling channels and venting systems help prevent defects like warping and burn marks.
- Mold Life Expectancy: The choice of mold material affects how long the mold will last before requiring replacement.
Investing in proper mold design ensures optimal performance, reducing defects and improving efficiency.
Mold Manufacturing Process
Creating an injection mold involves several steps, each requiring precision and expertise.
- Design Phase: Engineers create a CAD model of the mold, ensuring it meets design specifications.
- Machining: CNC machining, electrical discharge machining (EDM), and grinding shape the mold components.
- Assembly: Mold components are assembled, ensuring proper fit and function.
- Testing (T1-Tn Trials): Initial mold trials identify potential defects and allow for adjustments.
- Production and Maintenance: Once finalized, the mold enters full-scale production with routine maintenance to ensure consistent performance.
This process ensures that molds are built to exact specifications for efficient and defect-free production.
Cost of Injection Mold Tooling
Injection mold tooling costs vary widely depending on several factors.
- Prototype Molds: $5,000 - $20,000, suitable for testing and small production runs.
- Production Molds: $20,000 - $500,000+, depending on complexity and material selection.
- Factors Affecting Cost:
- Number of cavities
- Mold material
- Part complexity and size
- Expected production volume
While mold tooling is a significant investment, high-quality molds can last for millions of cycles, making them cost-effective in the long run.
Common Injection Molding Defects and Solutions
Injection molding defects can impact product quality and increase production costs. Here are some common issues and their solutions.
- Warping: Caused by uneven cooling, it can be prevented by improving mold design and material selection.
- Flashing: Excess plastic at the parting line due to improper clamping or mold wear. Fixing mold alignment helps prevent this issue.
- Short Shots: Incomplete filling of the cavity due to insufficient pressure or poor material flow. Adjusting injection speed and pressure can resolve this problem.
- Burn Marks: Dark spots on the surface caused by overheating or poor venting. Optimizing vent placement and reducing injection speed can help.
Addressing these defects early ensures high-quality production with minimal waste.
Future Trends in Injection Mold Tooling
The injection molding industry is constantly evolving with new technologies that enhance efficiency and sustainability.
- 3D Printed Molds: Used for rapid prototyping and low-volume production, reducing lead times and costs.
- Automated Mold Maintenance: Sensors and AI-driven predictive maintenance extend mold life and prevent unexpected failures.
- Sustainable Molding: Recyclable materials and energy-efficient cooling systems reduce environmental impact.
- AI and Simulation Tools: Advanced software optimizes mold design, cycle times, and material usage.
These innovations are driving the industry toward faster, more cost-effective, and environmentally friendly production.
Conclusion
Injection mold tooling is a vital aspect of manufacturing, enabling the mass production of high-quality plastic parts with precision and efficiency. From selecting the right mold type and material to optimizing design and maintenance, every step in the process plays a crucial role in ensuring successful production.
Investing in high-quality molds, advanced manufacturing techniques, and continuous improvements in design and maintenance can lead to significant cost savings and enhanced product quality. As technology advances, businesses that stay ahead of the curve will benefit from greater efficiency, reduced waste, and improved sustainability in injection molding.
Whether you're new to injection molding or looking to refine your processes, understanding the fundamentals of mold tooling will help you make informed decisions and achieve optimal results.





