Plastic Molding Design: 7 Critical Parameters
If someone took plastics out of our daily life, we would be left with a big void-unfillable by anything else. Plastics have become so common in our life that we often don’t know the complex process of plastic molding design that stands behind the manufacture of every single plastic part.
Be it the plastic cap on your water bottle or the plastic chair you sit on-every single plastic part goes through an extensive process of designing.
You May Also Read: Identifying the Plastic Molding For in Chain Process Parameters
Plastic molding design is a meticulous process that forms the basis of the entire injection molding procedure. Plastic molding designers need to have a thorough knowledge of all the critical parameters of the molding process to craft the perfect part. One of these critical parameters is the distance parameter.
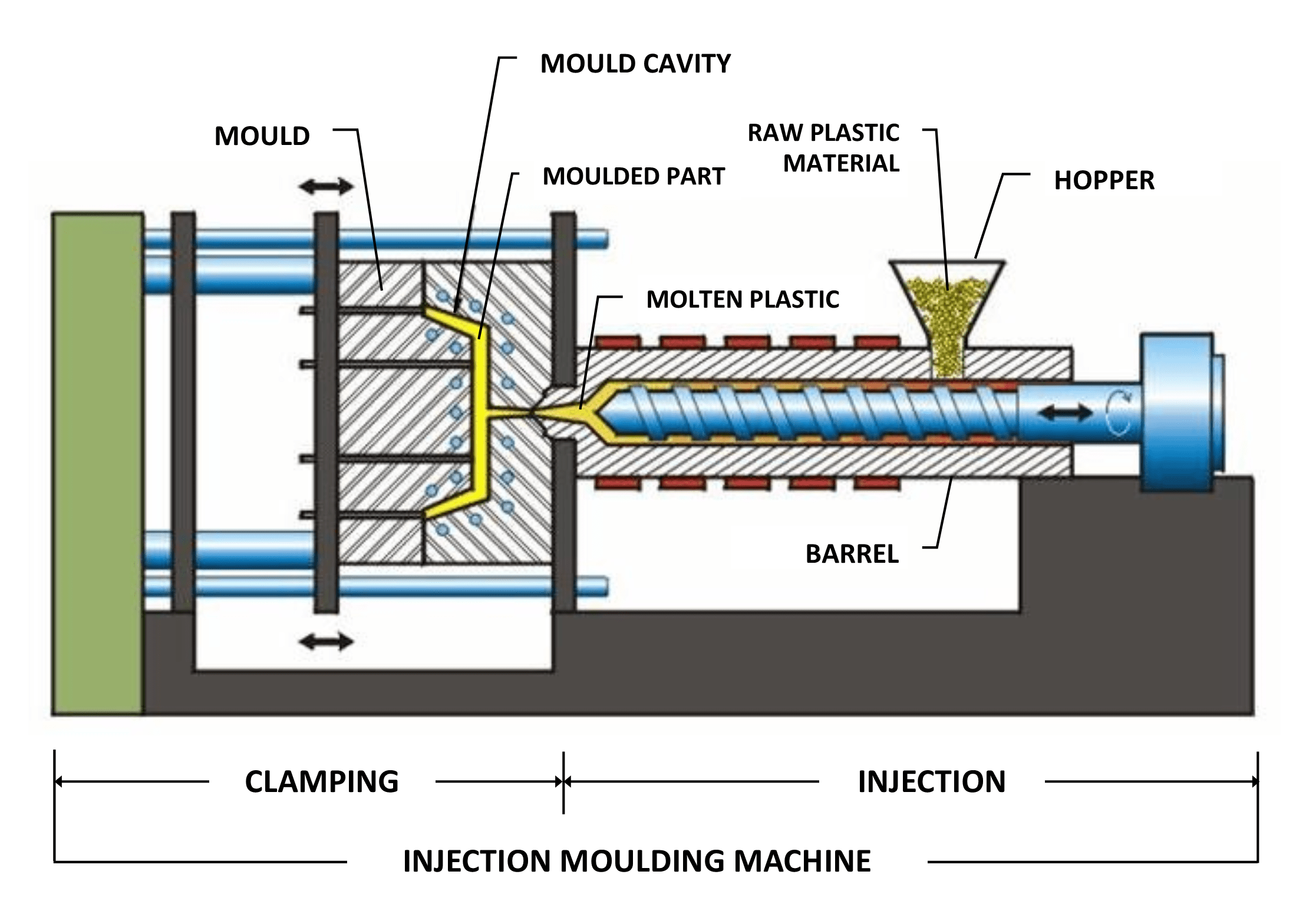
What is Plastic Molding?
Before we dive into the importance of the distance parameter in the plastic molding design process, let us shed some light on what plastic molding is.
Plastic molding utilizes granular plastic as raw material and converts it into well-shaped plastic parts. By magic? No, by an intricate process of clamping, melting, injecting, holding, and cooling.
Molders feed granular plastics in the barrel of the moulding machine. A screw pushes the molten plastic forward and injects it into the mold cavity. The molten plastic occupies the cavity and takes its shape. The machine then allows the plastic to cool for a few seconds.
After the cooling stage, the mold opens up, and ejector pins push the plastic part out of the cavity. Then the mold closes back and completes one cycle of the plastic molding process.
Understanding Plastic Molding Design
Plastic molding is not as easy and straightforward as it seems. Each part of the plastic molding process needs to be in sync with its preceding and succeeding step. This synchronization ensures the production of high-quality plastic parts consistency and efficiency.
Molders first design the entire process in detail to synchronize all the steps of plastic molding,
The process of plastic molding design encompasses three procedures; part design, mold design, and process design. All three of these designing procedures go hand-in-hand. Such that one process cannot reach completion without another.
A complete plastic molding design will optimize every single step of the plastic molding process according to the parts specification and mold capabilities.
Essential Parameters: The Distance Parameter
Several parameters demand thorough consideration while the plastic molding designing process.
You’ll see parameters such as wall thickness, draft angle, and various temperatures and pressures topping the list of critical parameters. However, there is an entire range of parameters that are very important in plastic molding design. These are the distance parameters. Let us have a look at what these distance parameters are and what role they play in the designing process.
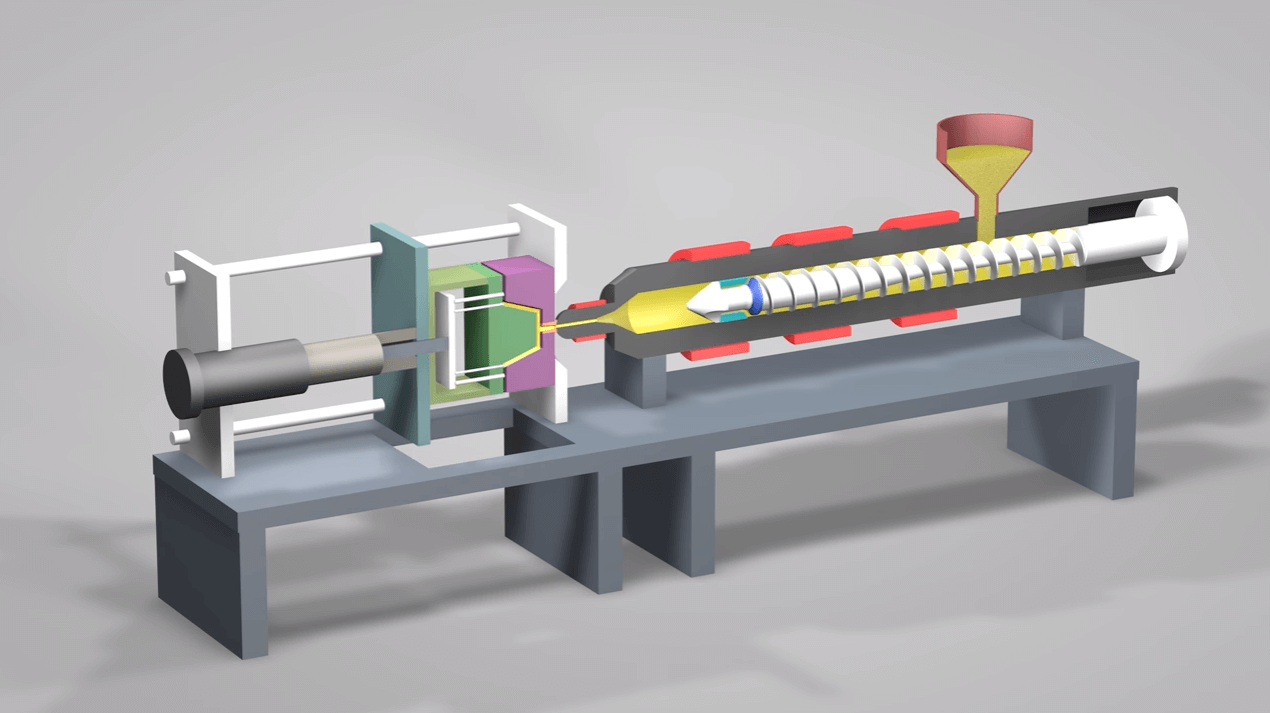
1. Mold Close Distance
A typical injection molding machine mold has two plates. One of these plates-plate A-is immobile. While the other plate-plate B- is movable and responsible for opening and closing the plate.
The distance that plate B travels to close the mold after it has removed the molded part is called the mold close distance.
Once the mold closes, the next cycle can start, therefore the mold close distance is a crucial parameter. It can increase or decrease cycle time which can increase or decrease the productivity of the plastic molding process.
2. Injection Distance
The injection molding process employs a screw-type plunger that injects the molten plastic into the cavity of the mold. Injection distance is the distance that the plunger covers when hydraulic back pressure pushes it forward to fill the cavity with the molten polymer.
If the injection distance is inappropriate, the machine may inject more or less than the required amount of plastic. Which can result in defects such as flash or burrs or flow marks on the plastic part.
3. Injection Hold Distance
After the machine injects molten plastic into the mold, a packing/holding stage ensues. In this stage, pressure is applied to the mold to make the molten plastic take the exact shape of the cavity. This pressure is applied by pushing more molten plastic through the mold.
The screw-plunger moves forward from its point of injection to push some additional amount of plastic into the mold. The distance it travels from the point of injection to the point of addition of ‘push material’ is called the injection hold distance. The screw stays in this position while the hold stage lasts and then moves back for recovery.
In case the injection holding distance is too big, it will fail to exert enough holding pressure. And low holding pressure can result in sink marks or voids on the plastic part.
4. Cushion
As we mentioned before, the plastic molding machine injects additional molten plastic into the mold to exert pressure on the melt present in the cavity. This molten plastic is called a Cushion. Most molders refer to it as ‘the pathway’ of pressure that enables the packing and holding process.
Without a Cushion, the machine will not be able to exert pressure on the part inside the cavity. And this can result in the production of misshaped plastic molded parts.
5. The Screw Return Distance
Screw return distance or screw recovery distance is the distance that the screw-type plunger travels back after it is done pressurizing the molten plastic present in the cavity and prepare for the next shot of molten plastic.
This screw return distance must be such that the screw takes enough time to travel back. It is crucial so that the previous shot of molten plastic cools and ejects from the mold before the plunger injects the next shot.
Screw distance is a critical parameter that, if not set right, can delay the cycle initiation and hence increase cycle time. Therefore, while plastic molding design, the designers must determine how much time the plastic part will take to cool and eject and must set the screw return distance appropriately.
If the screw recovery distance does is small, it will inject the next shot before the mold opens, which will cause some of the molten plastic to drool out after the mold opens to eject the part.
6. Mold Open Distance
Mold open distance is another key parameter that the plastic molding design engineers and specialists must consider before they finalize the part and process design.
The mold open distance is the distance that Plate B travels back to open the mold and allow for the ejection of the part. As a best practice, the mold open distance should not be more than two times the thickness of the part.
If the mold distance is too long, the plate will have to travel longer. More extended travel will increase cycle time and decrease the cavity. However, if the mold distance is too thin, the ejected part may collide with the opposite plate and bear some damage.
Therefore, the designers must endeavor to define a mold open distance that does not delay their cycle time. While also ensuring safe ejection of part from the cavity.
7. Ejection Distance
Ejection distance can be defined as the distance that the ejector plates travel to move the ejection pins forward so that they push the molded part out of the cavity.
It is imperative for the molding distance should be optimal so that the ejection pins eject the part out within the time that the mold opens and closes.
EndNote
Many people refer to the process of plastic molding design as an art. However, it might be better if we look at it as a circumstantial synergy of art and science. The entire process of plastic molding design requires unified powers of part and mold designers and molders.
The plastic molding designer must have a thorough knowledge of all the parameters that are involved in the plastic molding process. A part that is designed while keeping all the critical parameters in mind is sure to have promising results.
Of all the essential parameters that need consideration, one set of parameters are the distance parameters. Many different parameters come under the heading of distance parameters.
These include mold open and close distances, Screw return distance and ejection distance, etc. Fine-tuning of all these parameters is of utmost importance because if even one of these goes awry, it can have impeding effects on the entire plastic molding process.
For more information on Plastic Molding, Contact Us Today.





