Injection molding is a manufacturing process in which plastic is melted and injected into a mold, where it cools and solidifies into the final product. There are many types of plastics that can be used in injection molding, including polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, ABS, and nylon. The choice of plastic will depend on the desired properties of the finished product, such as strength, flexibility, and heat resistance.
When it comes to manufacturing, injection molding is one of the most versatile and cost-effective processes available. It’s used to create a wide range of products, from automotive parts to medical devices. Injection molding is a great choice for mass producing parts with a consistent shape and size. But what’s the secret to successful injection molding? The answer is plastics - the key to unlocking the possibilities of injection molding.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the world of plastics for injection molding, from the different types of plastics used to the different molding processes and more. Read on to learn everything you need to know about plastic for injection molding and unlock the potential of this powerful manufacturing process.
What is Plastic Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process in which molten plastic is injected into a die or mold at high pressure and cooled to create a solid object. This process is used to create a wide range of products, from automotive parts to medical devices. The plastic injection molding process is fast and efficient, which makes it an ideal choice for mass production.
The process begins with a plastic resin, which is heated and injected into a mold at high pressure. The molten plastic is then allowed to cool and solidify into the desired shape. Once the plastic has cooled, it is ejected from the mold and is ready for use.
Benefits of Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding offers a number of benefits over other manufacturing processes. It’s a versatile process that can produce parts in almost any shape and size, making it ideal for mass production. Injection molding is also cost-effective and efficient, making it a great choice for large-scale manufacturing.
Injection molding also offers high precision and repeatability. The process allows for tight tolerances and creates highly detailed parts. This makes it an ideal choice for complex and intricate parts. Injection molding also has a high production rate, making it an ideal choice for high-volume production.
Types of Plastics Used for Injection Molding
Plastics are an essential part of the injection molding process. Different types of plastics are used for different applications, each offering their own unique advantages. The three main types of plastics used for injection molding are thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers.
Thermoplastics are the most common type of plastic used for injection molding. They are durable and can be melted and reused multiple times. Thermosets are plastics that are heated, cooled, and set into a permanent shape. They cannot be melted and reused like thermoplastics, but they offer higher strength and better heat resistance. Elastomers are flexible plastics that are often used for gaskets and seals.
Different Injection Molding Processes
The injection molding process is highly customizable, allowing for different processes to be used. The most common types of injection molding processes are gas-assist injection molding, reaction injection molding, and insert molding.
Gas-assist injection molding is a process in which pressurized gas is injected into the mold to fill the voids and provide better part accuracy. Reaction injection molding uses two different materials that are injected into the mold and allowed to react and form a solid part. Insert molding is a process in which inserts are placed into the mold before the plastic is injected.
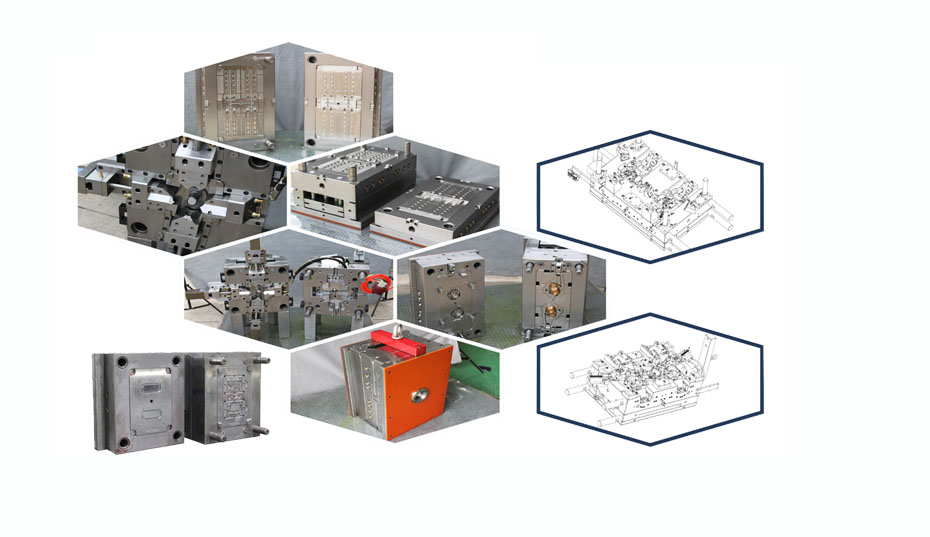
Molds Used in Injection Molding
Injection molds are the tools used to create the parts in the injection molding process. The molds are made from metal and can be reused for multiple runs of the same part. The molds are designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the injection molding process and create a consistent shape for each part.
The molds are created using CAD software and can be customized for each part. The molds are then machined from metal, typically from steel or aluminum. The molds are then tested and inspected to ensure they meet the specifications of the part.
Design Considerations for Injection Molding
Designing a part for injection molding is not as simple as designing a part for other manufacturing processes. There are several important design considerations that must be taken into account.
The most important consideration is the design of the mold. The mold must be designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the injection molding process. The design must also take into account the shrinkage of the plastic as it cools and the airflow needed to cool the part.
Other design considerations include wall thickness, draft angles, and undercuts. The wall thickness should be as consistent as possible to ensure the part is strong and uniform. Draft angles should be used to ensure the part can be easily removed from the mold. Undercuts should be avoided or minimized to make the mold easier to manufacture.
Post Injection Molding Processes
Once the part is ejected from the mold, there are still several post injection molding processes that can be used to improve the part. Post injection molding processes include painting, plating, and assembly.
Painting and plating are often used to improve the appearance and durability of the part. Painting can also be used to add branding or logos to the part. Assembly is used to combine multiple parts into a single product. This can be done using adhesives, rivets, or other fastening methods.
Quality Control
Quality control is an essential part of the injection molding process. Quality control processes help to ensure that the parts meet the specified requirements and are free from defects. Quality control processes can include visual inspection, dimensional inspection, and testing.
Visual inspection is used to identify any defects in the part’s appearance. Dimensional inspection is used to measure the dimensions of the part and ensure it meets the specified requirements. Testing is used to test the performance of the part and ensure it meets the specified requirements.
Cost Considerations
Cost is an important consideration when it comes to injection molding. The cost of injection molding depends on several factors, including the size and complexity of the part, the material used, and the number of parts being produced.
The cost of the mold is one of the most important cost considerations. The cost of the mold depends on the size and complexity of the part, as well as the number of cavities in the mold. The cost of the plastic resin is another important cost consideration. The cost of the plastic depends on the type of plastic being used and the quantity being used.
Tips and Tricks for Injection Molding
Injection molding is a powerful manufacturing process, but it can also be a tricky one. Here are some tips and tricks to help you get the most out of your injection molding process.
First, make sure to design the part and mold with the injection molding process in mind. Design the part to minimize wall thickness variations and avoid undercuts. Also, design the mold to minimize the number of cavities and minimize cycle time.
Second, choose the right plastic for the job. Different plastics have different properties, so make sure you choose the right one for the part. Third, use a high-quality molding machine and keep it properly maintained. This will ensure the injection molding process runs smoothly and efficiently.
Conclusion
Injection molding is a powerful and versatile manufacturing process. The key to successful injection molding is plastics - the key to unlocking the possibilities of injection molding. From the different types of plastics used to the different molding processes and more, this comprehensive guide has covered everything you need to know about plastic for injection molding. Now that you’ve read this guide, you’re ready to unlock the potential of injection molding and create parts with precision and accuracy.





