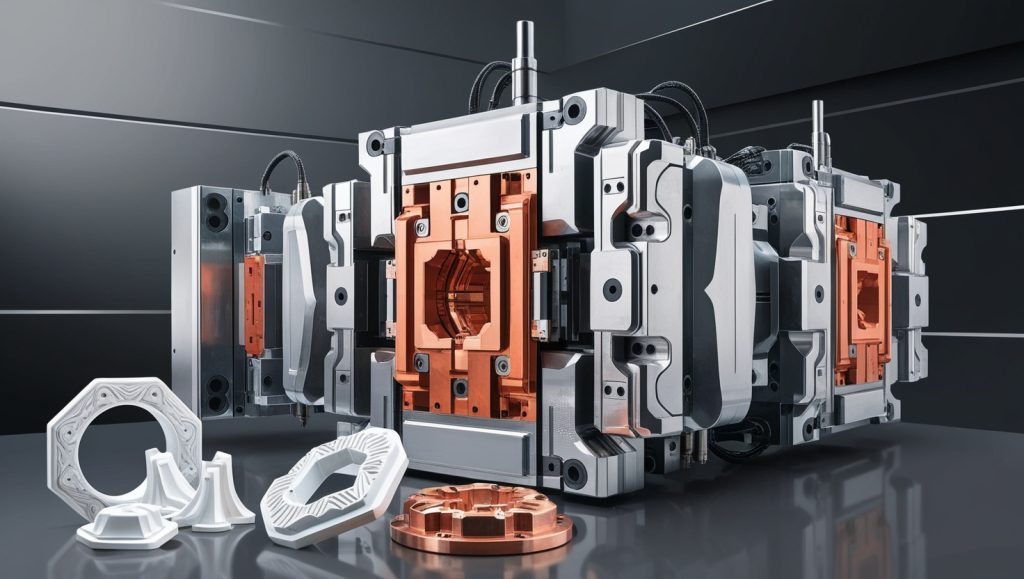
Plastic tooling plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing, enabling the production of intricate and highly precise components for various industries. From automotive parts to medical devices, the demand for complex plastic shapes continues to rise, pushing manufacturers to develop advanced tooling techniques to maintain accuracy and efficiency.
As technology evolves, plastic tooling has become more refined, allowing for the creation of detailed and customized components. However, producing complex plastic shapes comes with its own set of challenges, including material selection, tooling costs, and production constraints. Understanding the techniques and considerations involved in plastic tooling is essential for achieving high-quality results.
This article explores the methods used in plastic tooling for complex shapes, covering key techniques, design factors, challenges, and advancements shaping the industry.
Understanding Plastic Tooling
Definition and Purpose
Plastic tooling refers to the process of designing and manufacturing molds or tools that shape plastic materials into desired forms. These tools are essential for mass production, ensuring consistency, durability, and precision in plastic components. Depending on the production method, tooling can involve intricate designs and high-precision requirements.
Different Types of Plastic Tooling
Plastic tooling methods vary based on the manufacturing process. Some common types include:
- Injection Molding Tools – Used to inject molten plastic into a mold cavity, ideal for high-volume production.
- Thermoforming Tools – Used to shape heated plastic sheets over a mold using vacuum or pressure.
- 3D Printing Molds – Utilized for rapid prototyping and small-scale manufacturing through additive processes.
- CNC Machining Tools – Used to carve plastic sheets into complex designs with high precision.
Comparison with Metal Tooling
While metal tooling is often associated with durability and heavy-duty applications, plastic tooling offers several advantages, including:
- Lower production costs
- Faster prototyping and design modifications
- Lightweight and versatile material options
- Reduced energy consumption during processing
Challenges in Plastic Tooling for Complex Shapes
Manufacturing complex plastic shapes presents several technical and design challenges:
- Intricate Geometries – Creating highly detailed designs without defects such as warping or shrinkage can be difficult.
- Material Compatibility – Choosing the right plastic for durability, flexibility, and heat resistance is critical.
- Production Costs – Tooling and material costs must be balanced with precision requirements to remain cost-effective.
- Tool Wear and Maintenance – Complex molds require maintenance to prevent defects and ensure longevity.
Types of Plastic Tooling Techniques
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely used plastic tooling method where molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. This process is ideal for producing detailed and consistent components at a large scale.
Best Suited Applications
- High-volume manufacturing
- Precision components with intricate details
Advantages
- High accuracy and repeatability
- Compatible with various plastic materials
- Efficient for mass production
Limitations
- High initial tooling costs
- Limited design modifications once the mold is created
Thermoforming
Thermoforming involves heating a plastic sheet until it becomes flexible and then shaping it over a mold using vacuum or pressure. This method is commonly used for creating large plastic components.
Benefits
- Cost-effective for large plastic parts
- Quick production cycles
- Lower tooling costs compared to injection molding
Drawbacks
- Limited to thinner plastic sheets
- Less suitable for highly detailed or intricate components
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
3D printing has revolutionized plastic tooling by offering greater flexibility in design and the ability to create complex geometries without traditional molds. It is commonly used for prototyping and low-volume production.
Key Benefits
- No need for traditional molds, reducing costs for short runs
- High design flexibility for complex and intricate shapes
- Faster prototyping and development cycles
Limitations
- Slower production times for large-scale manufacturing
- Limited material choices compared to injection molding
CNC Machining for Plastic Tooling
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that carves plastic components from a solid block using precision tools. It is commonly used for creating high-precision parts that require durability.
Pros
- High accuracy and detail for complex designs
- Suitable for durable plastic components
- No need for expensive molds
Cons
- Higher material waste compared to other methods
- Can be expensive for large-scale production
Design Considerations for Complex Shapes
Material Selection
Choosing the right plastic material is critical for achieving the desired performance in complex parts. Some commonly used plastics include:
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) – Strong and impact-resistant, suitable for automotive and consumer products.
- Polycarbonate – Offers high heat resistance and durability, often used in medical devices and safety equipment.
- Nylon – Provides flexibility and wear resistance, ideal for mechanical components.
- PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) – High-performance plastic with excellent chemical and heat resistance, used in aerospace and medical applications.
Mold Design and Complexity
When designing molds for complex plastic shapes, several factors must be considered:
- Core and Cavity Design – Ensuring the mold halves align perfectly to create accurate parts.
- Draft Angles – Allowing for easy removal of parts from the mold without damage.
- Undercuts and Side Actions – Handling intricate features that require additional tooling mechanisms.
Shrinkage and Warping Issues
Plastics tend to shrink as they cool, which can lead to warping or dimensional inaccuracies. To minimize these issues:
- Use uniform wall thickness in designs
- Incorporate rib structures to reinforce stability
- Control cooling rates during production to reduce internal stresses
Advanced Technologies in Plastic Tooling
Innovations in plastic tooling continue to enhance efficiency and precision:
- AI-Driven Design Optimization – Software tools use AI to refine mold designs and improve manufacturability.
- Automation in Mold-Making – Robotic systems enhance consistency and speed in production.
- Rapid Prototyping – Faster iteration cycles using 3D printing and hybrid manufacturing techniques.
Cost-Effective Strategies for Complex Plastic Tooling
Balancing cost and quality is essential in plastic tooling. Some strategies include:
- Optimizing mold designs to reduce material waste
- Using modular tooling for flexible production
- Implementing lean manufacturing practices to minimize production costs
Applications of Complex Plastic Tooling
Complex plastic tooling is widely used across various industries:
- Automotive – Lightweight and durable plastic parts for interiors and exteriors.
- Medical Devices – High-precision plastic components for surgical tools and implants.
- Consumer Products – Custom plastic enclosures for electronics and household goods.
- Aerospace and Defense – Heat-resistant and high-strength plastic parts for aircraft and military applications.
Case Studies of Successful Plastic Tooling Projects
Examining real-world examples of successful plastic tooling projects provides insights into best practices and innovative solutions. Companies have leveraged advanced tooling techniques to enhance product quality, reduce costs, and improve production efficiency.
Future of Plastic Tooling for Complex Shapes
The future of plastic tooling is evolving with emerging technologies:
- Greater adoption of automation and AI in design and production
- Increased use of sustainable and biodegradable plastics
- Enhanced hybrid manufacturing methods combining traditional and digital techniques
Conclusion
Plastic tooling for complex shapes continues to advance, offering manufacturers new ways to produce high-precision components efficiently. With improvements in technology, material selection, and design processes, the challenges associated with complex plastic tooling are becoming more manageable. Understanding the best techniques and considerations for plastic tooling ensures optimal results in various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is plastic tooling, and why is it important for complex shapes?
Plastic tooling refers to the process of designing and manufacturing molds or tools used to shape plastic materials into desired forms. It is crucial for producing complex shapes with high precision, ensuring consistency, durability, and cost-effective mass production.
2. What are the best plastic tooling methods for intricate designs?
Injection molding and 3D printing are among the best methods for intricate plastic designs. Injection molding offers high accuracy and efficiency for large-scale production, while 3D printing allows for greater design flexibility and rapid prototyping. CNC machining is also effective for precision parts.
3. What factors should be considered when designing molds for complex plastic parts?
Key factors include material selection, draft angles for easy removal, uniform wall thickness to prevent warping, and the inclusion of undercuts and side actions for intricate features. Proper mold cooling and venting also play a role in achieving high-quality parts.
4. How can manufacturers reduce costs in plastic tooling for complex shapes?
To minimize costs, manufacturers can optimize mold designs to reduce material waste, use modular tooling for flexibility, implement lean manufacturing practices, and leverage automation and AI-driven design optimizations to streamline production.
5. What are the future trends in plastic tooling for complex shapes?
Future trends include increased automation in mold-making, AI-driven design optimizations, sustainable plastic alternatives, and hybrid manufacturing techniques that combine traditional molding with digital fabrication methods like 3D printing. These advancements aim to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve sustainability.





